DRAFT- InProgress
Abstract
Commentary:
The App Directory (AppD) is a service that provides a financial application definition that includes a trusted identifier(s) and associated metadata. The information registered as part of an application definition supports discovery, launch configuration, intents and context data supporting the use and interoperability of financial applications. This proposal recommends use of a distributed or detached model to managing application data servicing, where there are (N) AppD services on a network providing information related to a subset of namespace "zones" that align with the financial application identifiers. This approach encourages independence, scale and responsive provisioning of application definitions. This is modeled from a subset of the public name service "Domain Name System", which has proven reliable and conceptually fit for discovery.
In order to support the discovery of application data stored in a given directory, name space concepts are introduced to both identify the realm of application definitions and AppD service locations that host data. In simple terms, there has to be a way of discovering the location of the AppD service itself and the associated application definitions that are available from that service.
This proposal focuses on defining the following key features to support this need:
- Application data discovery through nested namespace approach. (Note: An expanded definition is required outside this proposal)
- AppD service host discovery implementations should support the following requirements;
- Discovery through use of DNS SRV record types (RFC2782 ) - **Preferred
- Federated discovery of URI records between AppD services
- Statically defined URI records for use within client applications directly
The key words "MUST", "MUST NOT", "REQUIRED", "SHALL", "SHALL NOT", "SHOULD", "SHOULD NOT", "RECOMMENDED", "MAY", and "OPTIONAL" in this document are to be interpreted as described in BCP 14, RFC 2119 [RFC2119].
Examples:
AppD service through DNS / SRV records:
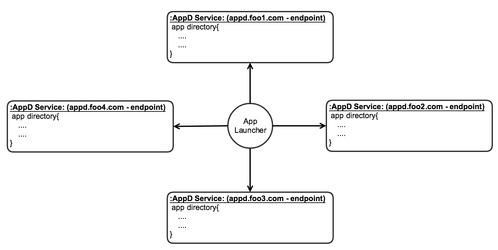
AppD Service distribution visual:
Proposal
Application data discovery
For the purposes of this proposal, application data discovery shall be accessible through a unique identifier representing a single application represented by a nested namespace syntax using dot notation (e.g. app.sub.root). It should be noted that a given AppD service may support multiple application namespace "zones" as part of a standard nested naming hierarchy.
Example:
getAppData("app.sub.root")
return
{
"guid": "app.sub.root",
"id":1,
"name":"app",
"title":"A really cool app",
"manifest_url":"https://app.sub1.root/app.json",
"description":"An app that provides really cool financial data",
"contact_email":"info@app.sub.root",
"support_email":"support@app.sub.root",
"signature":"https://prod.match.autilla.com",
"publisher":"openfin",
"icon":"https://app.sub.root/img/1525196540430.jpg",
"appPage":"/apps/app",
"images":[
{
"url":"https://app.sub.root/img/1525196540315.png"
}]
}
Host discovery
The following represents the three ways AppD service instances should be discovered over a given network. Again, the view is that AppD services are distributed/decoupled based on associated application namespace on a given network. This takes into account the use of the application identifiers described in previous section.
DNS/SRV Records
The use of a well known proven name service system to support the resolution of AppD service locations is the recommended approach to supporting discover of a
.png?version=1&modificationDate=1526225537735&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&width=973&height=250)